The working processes of Cable Ladder, Cable Tray, and Central Air Conditioning (AC) systems are crucial aspects of electrical and mechanical projects. Here’s a detailed explanation of how these systems function and are implemented, tailored for Entrepreneur Power Engineering:

A cable tray system is used for supporting insulated cables, power cables, and communication cables. It is ideal for managing medium to light cable loads in commercial and industrial setups
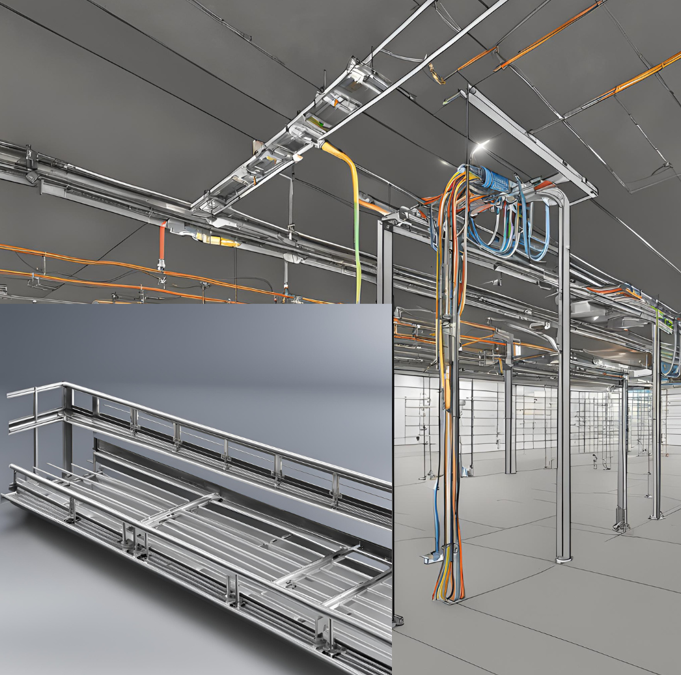

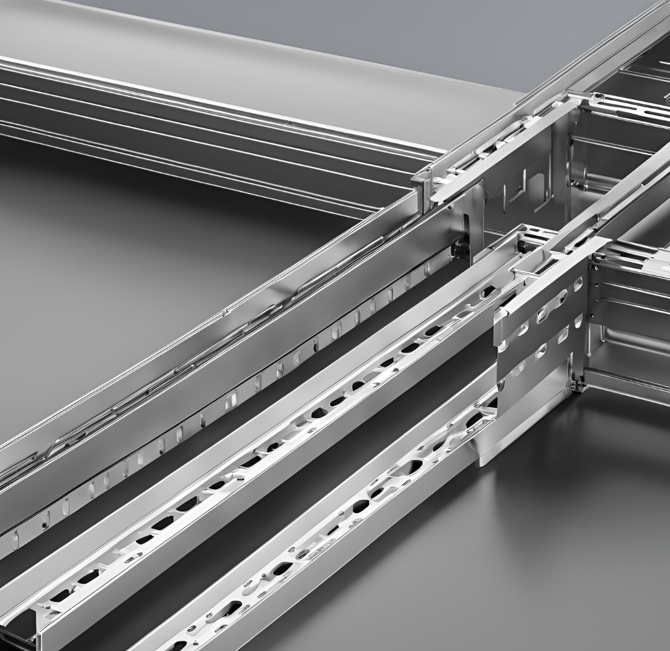
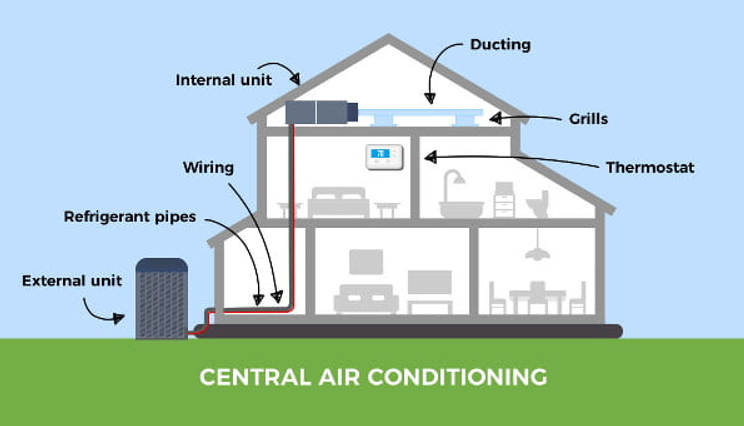
Key Advantages of These Systems
Entrepreneur Power Engineering’s Role

Entrepreneur Power Engineering has become a trusted leader in the industries have successfully completed numerous projects in civil construction, architectural design, renewable energy, and infrastructure development, earning the satisfaction and trust of our clients.